Contingent upon the overall patient’s health and the use of other prescribed drugs or potent chemotherapy, fenbendazole dosage measurements can change.
Dosage Manual:
Note: by chemotherapy treatment, extra supplements, natural items, nutraceuticals or drugs not identified with malignant growth therapy along with fenbendazole as well as to choose if fenbendazole alone could be taken to treat the disease of cancer, one ought to talk with proficient, authorized clinical advisor who has proper mentality and experience in the field of customary chemotherapeutic & combinatorial (elective) malignant growth treatment and experience in medicine compromise to avoid any unfavourable effects when consuming several medications/drugs together.
Proper fenbendazole Storage (powder; cases; tablets): under 25 °C, not presented to sun.
SIDE EFFECTS, TOXICITY AND FENBENDAZOLE METABOLISM
Harmfulness, genotoxicity and cancer-causing nature
It is difficult to assess the side effects and health implications of mild or high dosage fenbendazole might cause for people, as it’s anything but a medicine for individuals and there’s no past human-use history. It is hard to anticipate the results when extra medicine is taken along with fenbendazole.
The drug fenbendazole alone is exceptionally low acute toxic when had orally (estimated in rats and rodents). Oral exposure acute limit is not determined (it is possible that intense toxicity threshold may be above 5000mg material per kg body weight).
On the basis of human information, apparently portions of 500 mg for every individual didn’t bring about any antagonistic impacts. Moreover, single dosages of 2000 dose mg for every individual additionally caused no antagonistic impacts.
In view of an assortment of in vitro and in vivo tests for genotoxicity, where the European Medicine Agency had been included and somewhat dependable, it was resolved that fenbendazole isn’t genotoxic.
Proof for cancer-causing nature was discovered from a two-year research in mice.
Information about genotoxicity, toxic and cancer-causing nature recovered.
FENBENDAZOLE SIDE EFFECTS:
Some side effects of Fenbendazole are:
- Vomiting (uncommon)
- Diarrhea (uncommon)
- Jaundice (uncommon)
- Skin tingling (extremely uncommon)
- Liver injury (extremely uncommon)
METABOLISM OF FENBENDAZOLE:
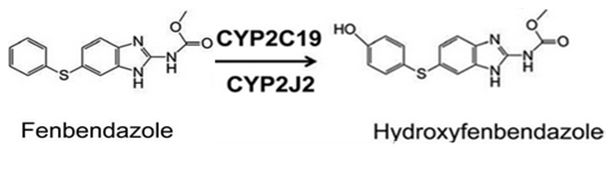
After absorption, two unique strides of fenbendazole body change happen – oxidation and hydroxylation.
The principal interaction occurs with the assistance of the two liver enzymes – CYP2C19 and CYP2J2. Fenbendazole gets hydroxylated and forms another metabolite – called hydroxy fenbendazole.
The subsequent cycle is the sulphide group oxidation. This is catalysed by enzymes CYP3A as well as monooxygenase that contain flavin, in the liver. Due to this, another new compound is formed- oxfendazole (which additionally shows anthelmintic and anticancer nature).
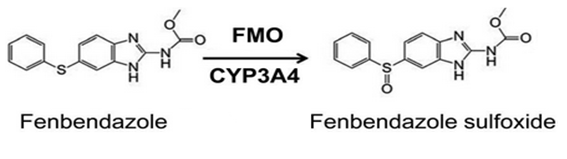
Amazingly, these discoveries propose that fenbendazole happens to be both a medication(drug) and a prodrug – it gives birth to one more active drug, produced metabolically.
It’s to be noted that fenbendazole doesn’t undergo 100% conversion over to metabolites because of its low bioavailability. Just a modest quantity of fenbendazole gets absorbed via the gastrointestinal tract. Eventually, fenbendazole, along with oxfendazole and hydroxy fenbendazole are discharged with defecation.
Remember! One enzyme utilized for using fenbendazole, CYP2C19, likewise is liable for drug metabolisms like amiodarone, tamoxifen, astemizole, ebastine, apixaban, mesoridazine, cyclosporine and thioridazine.
In the event that a patient suffering from cancer chose to consume one or a few of these medications along with bigger dosages of fenbendazole, one should reach her/his clinical advisor to obtain more data about the connections among fenbendazole along with these medications, conceivable extra side effects as well as probable elevated toxicity of the compound.

